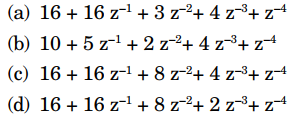GATE - 2009
1. Which of the following is a minimum-phase wavelet? The first value in each case is at time zero.
(a) {– 2, 5, – 2} (b) {– 2, 5, 2}
(c) {6, – 1, – 2} (d) {3, 4, – 4}
| (a) {– 6, 1, 1} (c) {– 1, 6, 1} | (b) {– 1, 1, 6} (d) {1, – 1, 6} |
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 3 and 4:
Given the wavelets, a = {3, – 2} and b = { 1, – 2}
3. The cross-correlation, \(\phi_{ab}\) is given by
(a) {– 6, 7, – 2} (b) {– 6, 10, – 12}
(c) {– 4, – 11, – 6} (d) {– 6, 11, – 4}
4. The inverse of wavelet ‘a', \(W_a^{– t}\) is given by
(a) {4/3, 16/9, 17/7, 64/81}
(b) { 1/3, 2/9, 4/27, 8/81}
(c) {4/9, 1/3, 64/81, 16/27}
(d) {16/27, 64/81, 4/9, 1/3}
5. Match the following functions in time-domain with their fourier spectra:
(b) P - 1, Q - 3, R - 2, S - 4
(c) P - 1, Q - 4, R - 2, S - 3
(d) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 3, S - 4
GATE 2010
1. An input signal {– 1, 1, 0.2}, after passing through a delay operator z, will be
(a) \(- z^2 + z^3 + 2z^5\) (b) {0, – 1, 1, 0, 2}
(c) {0, 2, 0, 1, – 1} (d) \( z + z^2 + 2z^4\)
2. The Hilbert transform of a function f (t) is denoted by H {f (t)}. If f (t) = sin t, then H{H(f (t))} is
(a) – sin t (b) – cost t
(c) sin t (d) cos t
(c) sin t (d) cos t
3. The rectangular function \(\pi(t)\) is defined as
\(\pi(t) =1 for \ |t|\le1/2\)
\(= 0 for \ |t|>1/2\)
The convolution of \(\pi(t)\) with itself will be
(a) a triangular function \(\Lambda(t)\) (b) \(\pi(t)\) again
(c) a unit-step function u(t) (d) a delta function \(\delta(t)\)
4. Given \(A= e^{-y}(cos x \ a_x – sin x \ a_y )\), where \(a_x\) and \(a_y\) denote the unit vectors in x- and y-directions, respectively. Then \(\nabla.(\nabla \times A)\) is equal to
(a) \(e^{-y}\) (b) 0
(c) \(e^{-y}(cos x)\) (d) \(e^{-y}(sin x)\)
5. Match the items in Group I with those in Group II.
Group I Group II
P. Convolution in 1. \(\frac{1}{2\Delta}\)
time domain
Q. Nyquist frequency 2. Flat spectrum
R. Aliasing 3. Multiplication in frequency domain
S. White noise 4. Frequency folding
5. Autocorrelation function
(a) P - 3, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 2
(b) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 5, S - 4
(c) P - 3, Q - 1, R - 2, S - 1
(d) P - 2, Q - 4, R - 1, S - 5
(b) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 5, S - 4
(c) P - 3, Q - 1, R - 2, S - 1
(d) P - 2, Q - 4, R - 1, S - 5
GATE 2011
1. The frequency of a signal sampled at 200 samples per second appears as 75 Hz. If the signal was under sampled, the frequency (in Hz) of the original signal would be
| (a) 100 (c) 150 | (b) 125 (d) 175 |
2. Match the items in Group I with those in Group II
Group I Group II
P. correlation in 1. reciprocal of total signal
frequency domain duration
Q. phase spectrum 2. aliasing
R. frequency interval 3. product of Fourier transform and its conjugate
S. undersampling 4. autocorrelation
5. Hilbert transform
(a) P - 3, Q - 5, R - 1, S - 2
(b) P - 3, Q - 4, R - 2, S - 1
(c) P - 3, Q - 4, R - 1, S - 2
(d) P - 2, Q - 3, R - 4, S - 5
(b) P - 3, Q - 4, R - 2, S - 1
(c) P - 3, Q - 4, R - 1, S - 2
(d) P - 2, Q - 3, R - 4, S - 5
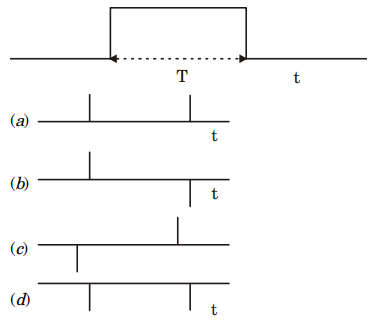
3. The derivative of the following boxcar function is
Common Data Questions
Common Data for Questions 4 and 5:
Common Data for Questions 4 and 5:
Time series P and Q are given by
P = {1, – 1, – 2, 0, 1}
Q = {1, 0, – 1}
4. The convolution of P and Q is
(a) {– 1, 0, 3, 1, – 3, – 1, 1}
(b) {1, – 1, – 3, 1, 3, 0, – 1}
(c) {1, – 1, – 3, – 1, 3, 1, – 1}
(d) {1, 0, 3, 1, – 3, – 1, 1}
5. P is similar and most out of phase to Q at a lag of
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) 2 (d) 3
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) 2 (d) 3
GATE 2012
Common Data QuestionsCommon Data for Questions 1 and 2
A signal having duration of 10 seconds is sampled at a rate of 1000 samples per second. The maximum frequency of the sampled signal is 475 Hz.
1. If t he signal has been under -sampled, the maximum frequency (in Hz) of the original signal would have been
| (a) 475 (c) 525 | (b) 500 (d) 550 |
2. What is the frequency interval (in Hz) at which the spectrum of the above signal is evaluated?
(a) 0.08 (b) 0.10
(c) 0.12 (d) 0.14
GATE 2013
1. Given a scalar function, f (x, y) = xy . The curl of gradient of f (x, y) is
(a) \(2x\hat{i}\) (b) \(-2y\hat{j}\)
(c) \(0\hat{i}\) (d) \(x\hat{i}+y\hat{j}\)
Common Data Questions
Common Data for Questions 2 and 3:
A recursive filter yn is given by \(y_n = 2x_n - x_{n-1} + y_{n-2}\).
2. The order of \(y_n\) is_________.
3. The transfer function of \(y_n\) in z-domain is
a) \(\frac{1-1.5z}{2-z^2}\) b) \(\frac{1-z^2}{2-1.5z}\)
c) \(\frac{2+z^2}{1+1.5z}\) d) \(\frac{1-1.5z}{2-z^2}\)
GATE 2014
1. The convolution of two finite length sequences xn = [1, 0, - 2] and yn = [1, - 1] is
(a) [-1, 1, 2, -2]
(b) [1, -1, -2, 2]
(c) [1, 0, -2, 2]
(d) [1, -2, -1, 2]
(b) [1, -1, -2, 2]
(c) [1, 0, -2, 2]
(d) [1, -2, -1, 2]
2. An 80 Hz seismic signal is sampled at a rate of 100 samples/s. What will be its aliased period (in seconds) in the sampled signal?
(a) 30 (b) 10
(c) 0.1 (d) 0.05
(c) 0.1 (d) 0.05
3. The Fourier transform and integral of the Dirac delta function respectively are
(a) 1 and 1 (b) 0 and 0
(c) 0 and 1 (d) 1 and \(\infty\)
4. A signal \(x_n\) = [2, 1] is input to a system whose impulse response is \(h_n\) = [8, 4, 2, 1]. The z-transform of the output is
GATE 2015
1. In any given signal, removal of all periods shorter than Nyquist period is achieved by
(a) high-pass filtering (b) band-pass filtering
(c) low-pass filtering (d) band-reject filtering
(c) low-pass filtering (d) band-reject filtering
2. The analytic signal for the function \(f(t)= sin \omega t\) is
(a) \(- cos \omega t\) (b) \(- sin \omega t\)
(c) \(e^{\omega t}\) (d) \(- e^{\omega t}\)
3. The minimum frequency at which a signal comprising of 30 Hz, 50 Hz and 70 Hz frequencies should be sampled to avoid aliasing is _______ Hz.
GATE 2016
1. Given a seismic wavelet w = { 6, – 4, – 2 } and reflectivity series r = { 0, 1, 0 }, the corresponding seismic trace is ___________.
(a) {0, – 4, 0, 0, 0} (b) {0, – 2, – 4, 6, 0}
(c) {0, 6, 0, 0, 0} (d) {0, 6, – 4, – 2, 0}
2. The time period of the signal \(s(t)= sin(\frac{\pi}{3}t) cos(\frac{\pi}{2}t) \), is ______ seconds.
3. Assertion (a): The inverse of a minimum phase wavelet is causal and stable.
Reason (r): The Z-transform of a minimum phase wavelet has all its zeros outside the unit circle.
(a) (a) is true but (r) is false
(b) (a) is false but (r) is true
(c) Both (a) and (r) are true and (r) is the correct reason for (a)
(d) Both (a) and (r) are true and (r) is not the correct reason for (a)
GATE 2017
1. Convolution of two box car functions of different widths yields a
(a) step function
(b) trapezoidal function
(c) box car function
(d) sinc function 45.
2. Assuming the Z-transform to be defined with Z as the unit delay operator, the pole of the infinite sequence \([1,\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{4},\frac {1}{8}]\) is at Z = _________.
GATE 2018
1. The formula for the ‘forward’ Fourier transform is \(F(\omega)=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}f(t) dt\) and that for the ‘inverse’ Fourier transform is \(f(t)=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}F(\omega) d\omega\) . Then, the forward Fourier transform of the function \(𝐹(\omega) = e^{-2i\omega}\) is
(a) \(2\delta(t)\) (b) \(\delta(2t)\)
(c) \(\delta(t + 2)\) (d) \(\delta(t – 2)\)
GATE 2019
1. If \(G(\omega)\) is the Fourier transform of \(g(t)\), then the Fourier transform of \(g(t + ln 2)\) will be
a)\(e^{-2j\omega}G(\omega)\)
b)\(e^{2j\omega}G(\omega)\)
c)\(2e^{j\omega}G(\omega)\)
d)\(2e^{-j\omega}G(\omega)\)
GATE 2020
1. The convolution of A(4, 2, –1, 2) with B (1, 0, –1) gives
(a) {– 4, 2, –5, 0, 1, 2 }
(b) { 4, 2, –5, 0, 1, –2 }
(c) {– 4, –2, 5, 0, –1, –2 }
(d) { 4, 2, 5, 0, –1, 2 }