GATE 2009
1.
GATE 2010
GATE 2011
GATE 2012
GATE 2013
GATE 2014
GATE 2015
GATE 2016
1. Depth migration is applied to a stacked seismic section. Compared to the stacked section, dipping events in the migrated section
(a) have a steeper slope and move updip.
(b) remain unchanged.
(c) have a gentler slope and move downdip.
(d) have a steeper slope and move downdip.
2. A monochromatic elastic wave of frequency 20 Hz propagates in a medium with average velocity 3 km/s. For zero offset reflection from horizontal reflectors, the thickness of the vertical first Fresnel zone is ________ m.
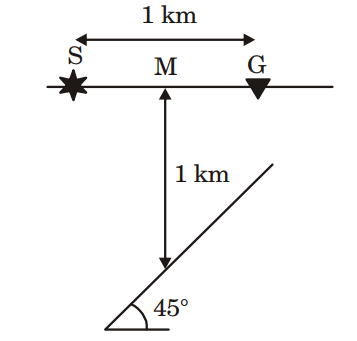
3. The following figure shows a seismic reflection experiment above a reflector that dips 45° . The P-wave velocity in the medium is constant and equal to 2 km/s. The source is kept at location ‘S’ and the receiver is kept at location ‘G’. The midpoint between S and G is denoted by ‘M’ and the depth to the reflector from ‘M’ is 1 km. The traveltime of the primary reflected arrival recorded at the receiver is equal to____ seconds.
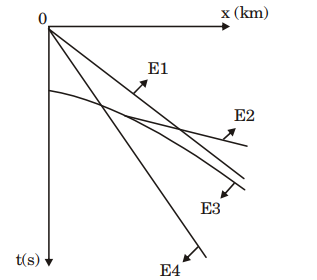
4. For land seismic data acquisition, the following figure is a schematic plot of arrival times of seismic waves recorded at several detectors placed along the x-axis. The shot is placed at the origin (x = 0).
Match the events labeled in the figure (listed in Group I ) with their corresponding types (listed in Group I I)
GATE 2017
1. A seismic reflection survey was carried out over a subsurface consisting of a stack of horizontal isotropic layers. In the common midpoint (CMP) domain, the moveout (travel time v/s offset) curve for any primary reflection event is best approximated by
(a) an ellipse (b) a parabola (c) a circle (d) a hyperbola
2. Normal movement (NMO) correction was applied to seismic data in the common midpoint (CMP) domain. The frequency distortion due to “NMO stretch” is highest for
(a) larger offsets of deeper reflections.
(b) smaller offsets of shallower reflections.
(c) larger offsets of shallower reflections.
(d) smaller offsets of deeper reflections.
3. Consider a hypothetical zero-offset seismic reflection survey acquired over a reflector whose dip is 30°. The velocity of the medium above the reflector is 2 km/s and the trace spacing is 25 m. The maximum unaliased frequency in the data is _________ Hz.
4. In statistical wavelet deconvalution, the reflectivity series is assumed to be a random sequence. Then, the autocorrelation of the wavelet is
(a) a scaled version of the autocorrelation of the seismic trace.
(b) a random sequence.
(c) zero.
(d) dirac-delta function.
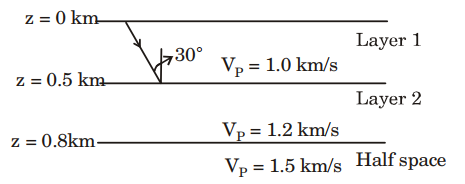
5. In the figure shown below, a ray corresponding to a P-wave is incident on the interface between layer 1 and layer 2 at an angle of 30°. The P-wave velocity is 1 km/s, 1.2 km/s and 1.5 km/s in layer 1, layer 2 and the half space, respectively. The emergence angle of the ray into the half space is _________ degrees.
6. How do the P-wave velocity (VP). S-wave velocity (V S), and Poisson’s ratio (\(\sigma\)) change fr om water saturated sandstone to a gas saturated sandstone?
(a) Vp increases, Vs decreases and \(\sigma\) increases.
(b) Vp decreases, Vs remains the same and \(\sigma\) decreases.
(c) Vp decreases, Vs increases and \(\sigma\) decreases.
(d) Vp, Vs and \(\sigma\) all remain constant.
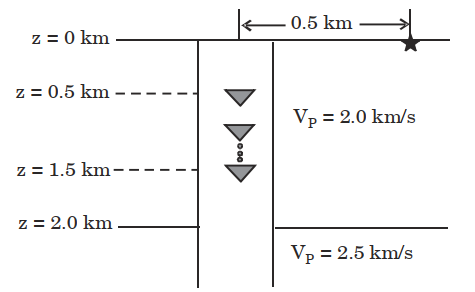
7. Consider a Vertical Seismic Profiling (VSP) data acquisition experiment as shown in the figure below. The subsurface consists of a horizontal layer of 2 km thickness underlain by a semi-infinite half-space. The P-wave velocities (VP) in the first layer and the half-space are 2.0 km/s and 2.5 km/ s, respectively. The vertical well has a string of receivers (denoted by inverted triangles) spaced 10 m apart, with the shallowest receiver at a depth of 0.5 km and the deepest receiver at a depth of 1.5 km. The source (denoted by star) is placed 0.5 km from the well head. The traveltime of the primary reflection event at the deepest receiver is ________s.
GATE 2018
1. The impulse response of the Kirchhoff pre-stack time migration operator for non-zero offsets in a homogeneous and isotropic medium is _______.
(a) a circle (b) a parabola (c) a hyperbola (d) an ellipse
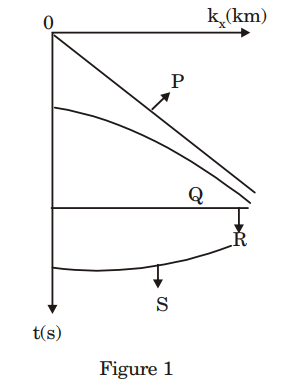
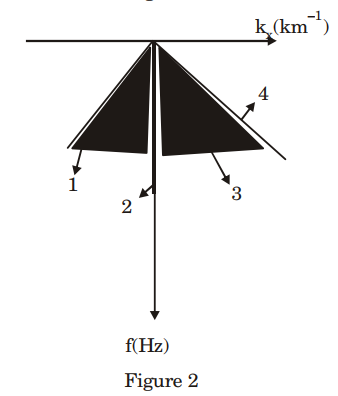
2. Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of four seismic events in t-x (time-offset) domain and Figure 2 is the result of transformation from t-x domain to fkx (frequency-horizontal wavenumber) domain. Match the events in t-x domain in Figure 1 with their counterparts in f-kx domain in Figure 2.
(a) P-1; Q-2; R-3; S-4 (b) P-1; Q-3; R-2; S-4 (c) P-4; Q-3; R-2; S-1 (d) P-4; Q-2; R-3; S-1
3. A horizontally travelling surface wave with a wavelength of 20 m is attenuated by a linear and uniform receiver array consisting of 4 receivers if the minimum receiver spacing is ________ m.
4. An end-on marine survey is carried out with equal and uniform shot and receiver spacing. If the total number of shots fired is 50 and a total of 10000 traces are recorded, the maximum fold for the survey is _______.
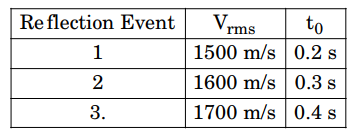
5. Consider a laterally homogeneous and isotropic ear t h model wi t h a fl at hor i zont al sur face and three hor izontal layers under lain by a halfspace. A seismic reflection survey was simulated on this model with the sources and receivers placed on the surface. The table below lists the root mean square (rms) velocities, V rms, and zero-offset two-way traveltimes t0 for the three reflection events from the bottom of each of the three layers observed in a pre-stack CDP (CMP) gather. The interval velocity of the second layer is _______ m/s.
GATE 2019
1. A reversed refraction survey was done over a two layered medium with the interface between them dipping at an angle of 15°. The velocities in the upper and lower medium are V1 and V2 respectively, with V2 > V1. If the critical angle is 45°, then, which one of the following isCORRECT? (V u and V d are updip and downdip velocities).
(a) V 1 = Vd = Vu (b) Vu > Vd > V1
(c) V 1 > Vd < Vu (d) Vu < Vd > V1
2. In a migrated seismic time section _______ .
(a) both synclines and anticlines appear tighter
(b) both synclines and anticlines appear broader
(c) synclines appear tighter and anticlines appear broader
(d) synclines appear broader and anticlines appear tighter.
3. A 3-D seismic tomography experiment was carried out with an inter-station spacing of ‘X’ km. The subsurface velocity perturbations in three dimensional blocks were estimated with block size of ‘2X’km and ‘0.5X’km in case 1 and case 2, respectively. Which one of the following statements is CORRECT?
(a) The spatial resolution is poor and variance is small for case 1.
(b) The spatial resolution is good and variance is small for case 2.
(c) The spatial resolution is good and variance is large for case 1.
(d) The spatial resolution is poor and variance is large for case 2.
4. A split-spread reflection survey is carried out along a profile in the direction of the dipping interface. The difference in arrival times of the reflected waves from the interface at two geophones with an offset distance of 1000 m from the shot-point on both sides is 20 msec. If the velocity of the layer above the dipping interface is 3000 m/s, then the dip of the bed is _______ degrees, (round off to 1 decimal place). (Assumption 2d >> X, where ‘d’ is depth below the shot-point normal to the interface and X is the source-geophone spacing)
5. A vibroseis source sweeps acoustic signal in the frequency range 10 Hz – 100 Hz. The maximum sampling interval to correctly recover the recorded signal will be _________ milliseconds.
GATE 2020
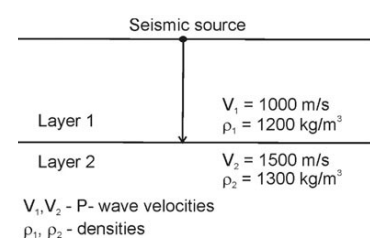
1. The transmission coefficient for the vertically incident seismic wave at the interface between Layer 1 and Layer 2 given in the figure is______. (Round off to 2 decimal places)
2. Assuming uncorrelated noise, the improvement in the signal to noise ratio in a reflection seismic survey with ‘n’ geophones spaced equally along the profile is proportional to(a) \(n\) (b) \(\frac{1}{n}\) (c) \(\sqrt{n}\) (d) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}}\)
3. A waveform with amplitude spectrum A (\(\omega\)) and phase spectrum \(\phi(\omega)\) is autocorrelated. Which one of the option given below correctly represents the information about the original waveform that can be retrieved from the autocorrelated waveform?
(a) A(\(\omega\)) can be retrieved but not \(\phi(\omega)\)
(b) \(\phi(\omega)\) can be retrieved but not A(\(\omega\))
(c) Both \(\phi(\omega)\) and A(\(\omega\)) can be retrieved
(d) Both \(\phi(\omega)\) and A(\(\omega\)) cannot be retrieved
4. In a 3D seismic survey, there are 512 groups of receivers in one line of a patch. Eight groups are moved per line from one patch to the next along the swath. What is the inline fold?
(a) 32 (b) 16 (c) 8 (d) 4
5. A sample of granite is observed to have a P-wave velocity of 5km/s and density of 2600kg/m3. The bulk modulus of the granite, assuming it to be a Poisson’s solid, is ______kilo-Pascal(kPa). (Round off to 2 decimal places)
6. A seismic reflection survey is carried out over a 1500m thick horizontal layer with a P-wave velocity of 2000m/s. The travel time of reflected wave at a surface detector placed 1000m from a surface source is ______ milliseconds.
7. A seismic reflection survey is carried out using a 10 milliseconds seismic wavelet over a subsurface medium having an average P-wave velocity of 1600m/s. The best resolution which is obtained on the basis of Rayleigh criteria is ______ m (Assume seismic wavelet contains one cycle)
8. A 10 Hz seismic wave propagates for 40 km through a material with a P-wave velocity of 5 km/s and quality factor (Q) of 100. The percentage of the initial amplitude retained in the attenuated wave is ________. (Round off to 1 decimal place) (Use \(\pi\) = 3.14)