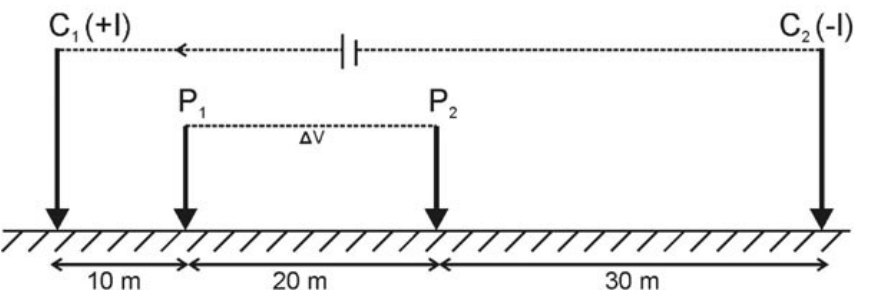
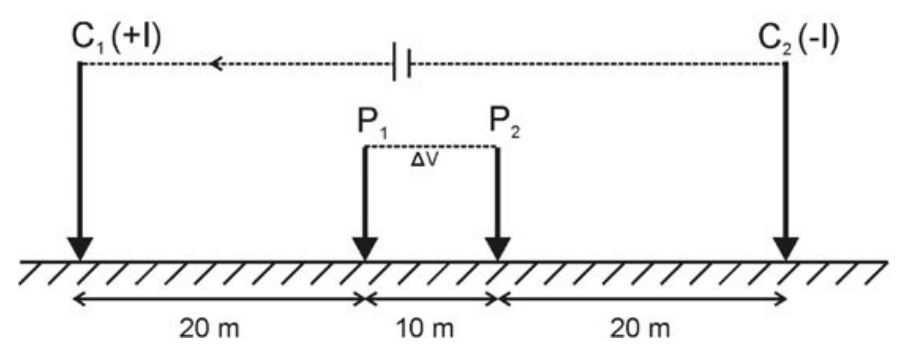
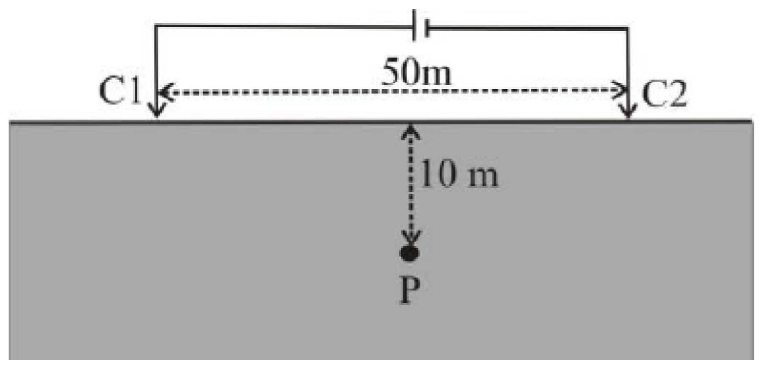
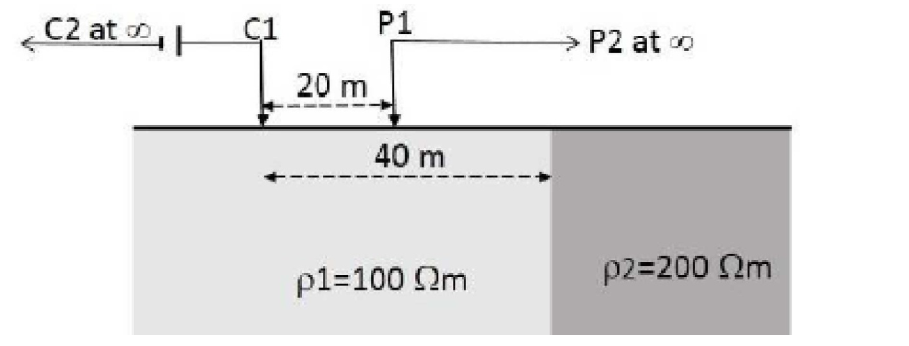
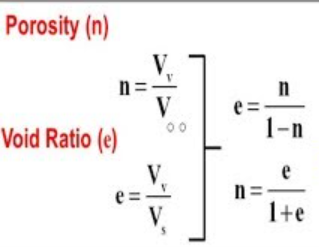
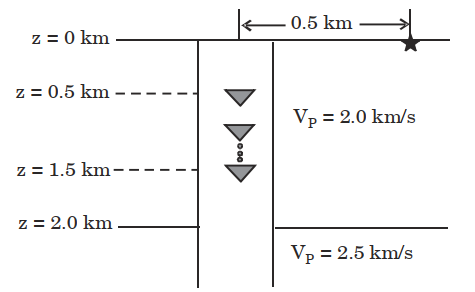
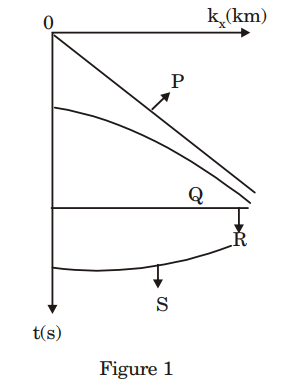
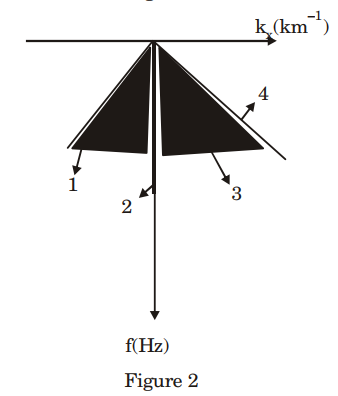
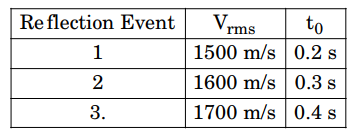
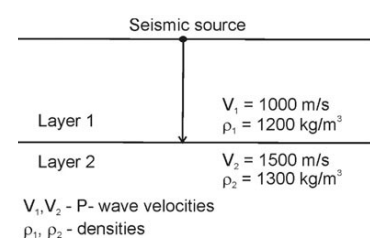
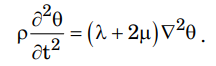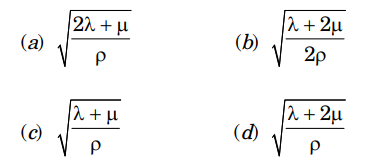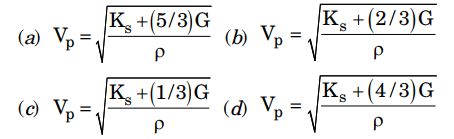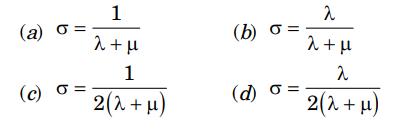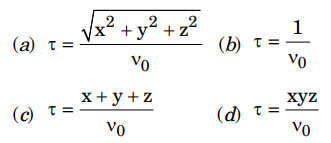3. The teleseismic rays are those that arrive at a seismometer for a distance greater than
4. Which is the parameter for measuring the size of the earthquake that does not need an instrumental record?
5. The standard form of wave equation for propagation of cubical dilatation (\(\theta\)) is
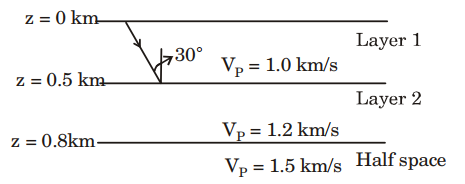
8. The seismic wave travelling in low velocity layer and critically incident at the discontinuity between low and high velocity layers
6. Snell’s law of refraction deals with which of the following properties of refracted waves?
(a) amplitude (b) direction (c) energy (d) phase
GATE 2012
1. Depth range of the ‘transition zone’ associated with phase changes in the Earth’s mantle is (in km)
(a) 35 to 150 (b) 150 to 410 (c) 410 to 660 (d) 660 to 800
2. The S-wave velocity in the lower continental crust is 6800 m/s and its density is 3380 kg/m3. Find its rigidity in GPa. (Give answer up to 2 decimal places)
(a) 156.29 (b) 160.21 (c) 162.34 (d) 500
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 3 and 4:
The seismic slip of a fault after an earthquake is measured to be 0.5 m and the fault area is estimated to be 250 km2 . The rigidity of the medium surrounding the fault is 30 GPa.
3. The seismic moment (in Nm) of the earthquake is
(a) \(3.75 \times 10^{18}\) (b) \(3.75 \times 10^{16}\) (c) \(3.75 \times 10^{14}\) (d) 3.75 \times 10^{121}\)
4. . Based on the above, the moment magnitude of the earthquake is
(a) 5.15 (b) 5.36 (c) 6.35 (d) 7.25
GATE 2013
1. Both strength and plasticity of a rock increase with the
(A) increase in temperature (B) decrease in strain rate
(C) increase in confining pressure (D) increase in pore fluid pressure
2. Amongst the following options, the acceptable value of the Poisson’s ratio of a rock is
(a) 0.55 (b) 1.00 (c) 0.25 (d) -1.00
3. The type of wave that arrives first at a station from an earthquake hypocenter is
(a) P-wave (b) S-wave (c) Rayleigh wave (d) Love wave
4. Which of the following is NOT an inverse square law?
(a) Newton’s law of gravitation (b) Coulomb’s law of electrostatics
(c) Coulomb’s law of magnetostatics (d) Hooke’s law
5. For seismic S-wave velocity, V, the rigidity modulus, µ, is proportional to
(a) \(\sqrt{V}\) (b) \(V\) (c) \(V^2\) (d) \(V^3\)
6. In a homogeneous anisotropic medium, the physical property varies
(a) with position but not with direction
(b) with both position and direction
(c) with direction but not with position
(d) neither with position nor with direction
7. Which of the following ways of measuring the size of an earthquake does not require instrumental recording?
(a) Richter magnitude (b) Moment (c) Mw (d) Intensity
8. Wadati diagram is a plot of the difference in P and S- wave arrival times against the arrival time of P-wave. It helps in estimating the
(a) velocity of P-wave. (b) velocity of S-wave.
(c) time of occurrence of earthquake. (d) hypocenter of earthquake.
GATE 2014
1. From the surface to the Earth’s interior, the velocity of P-wave decreases and the material density increases at the boundary between
(a) Outer core and inner core (b) Mantle and outer core
(c) Crust and mantle (d) Upper crust and lower crust
2. As compared to large earthquakes, small earthquakes are
(a) more frequent and caused by short fault slip and long rupture lengths
(b) more frequent and caused by long fault slip and short rupture lengths
(c) less frequent and caused by short fault slip and short rupture lengths
(d) more frequent and caused by short fault slip and short rupture lengths
3. For earthquakes of magnitudes 6 and 7, the seismic wave amplitudes are A 6 and A 7 and the radiated energies are E 6 and E 7 respectively. Which one of the following is true?
(a) \(A_7\approx \frac{7}{6} A_6 \ and \ E_{7}\approx10E_6\)
(b) \(A_7\approx 10 A_6 \ and \ E_{7}\approx100E_6\)
(c) \(A_7\approx 10A_6 \ and \ E_{7}\approx \frac{7}{6} E_6\)
(d) \(A_7\approx 10 A_6 \ and \ E_{7}\approx32E_6\)
4. The velocity discontinuity between the upper crust and the lower crust is known as __________ discontinuity.
(a) Lehmann (b) Gütenber (c) Mohorovicic (d) Conrad
5. The S-wave veloci t y of a medium havi ng a Poisson’s ratio and a P-wave velocity of 0.5 and 3 km/s respectively is _________km/s.
6. The PKiKP phase denotes the passage of a seismic wave in the Earth as
(a) P in mantle, S in outer core, reflected as P from inner-outer core boundary, S in outer core, P in mantle and crust
(b) P in crust, P in mantle, reflected as P from core-mantle boundary, P in mantle, P in crust
(c) P in mantle, P in outer core, P in inner core, P in outer core, P in mantle and crust
(d) P in mantle, P in outer core, reflected as P from inner-outer core boundary, P in outer core, P in mantle and crust
GATE 2015
1. PcP and ScS phases are reflected from
(a) crust - mantle boundary
(b) core - mantle boundary
(c) inner core - outer core boundary
(d) lithosphere - asthenosphere boundary
2. Gardner’s formula relates the seismic P-wave velocity (VP ) to
(a) density (b) porosity (c) permeability (d) lithology
3. Analysis of data from a 3-component broadband seismological station yields seismic velocities, Vp = 7.0 km/s and Vs = 3.87 km/s for the lower crust. The resulting Poisson’s ratio of the lower crustal rocks (rounded to two decimal places) is
(a) 0.24 (b) 0.26 (c) 0.28 (d) 0.30
GATE 2016
1. Which one of the following layers of the Earth has the largest volume?
(a) Upper Mantle (b) Lower Mantle (c) Outer core (d) Inner Core
2. The S-wave shadow zone of the Earth ranges from ________.
(a) 103° to 180° (b) 103° to 160° (c) 103° to 153° (d) 103° to 143°
3. Which one of the following is the ray path for the P-wave that converts to S-wave while passing through the solid inner core?
(a) PKiKP (b) PKIKP (c) pPcP (d) PKJKP
4. Which one of the following statements is CORRECT for the stress drop (\(Delta \sigma\)) of an earthquake?
(a) Large slip on a small fault will cause more stress drop.
(b) Small slip on a large fault will cause more stress drop.
(c) Stress drop is inversely proportional to the slip of the fault.
(d) Stress is directly proportional to the rupture dimension.
5. The energy released by an earthquake of magnitude 7 is ________ times the energy released by an earthquake of magnitude 4 (use Kanamori’s formula).
GATE 2017
1. A seismic gap refers to a
(a) time gap between two great earthquakes.
(b) distance gap between the epicenters of two great earthquakes.
(c) segment of an active belt where a historical great earthquake has no occurred.
(d) wide gap in the earth created by a great earthquake
2. The travel time difference between the arrival times of a shear wave (S) and primary wave (P) observed on a seismogram recorded at an epicentral distance of 100 km from a near surface earthquake is _________s.
(Assume the average P and S wave velocities to be 6.0 km/s and 3.5 km/s, respectively).
3. The percentage increase in P-wave velocity (km/ s) across the Mohorovicic discontinuity from the lower crust to the upper mantle beneath craton is approximately ___________(%).
4. Which one of the following seismic phases is observable in the P-wave shadow zone?
(a) P (b) PmP (c) PcS (d) PKiKP
5. Which one of the following statements is TRUE for near surface earthquake occurring in a homogeneous, isotropic Earth?
(a) Rayleigh wave are generated (b) Love waves are generated.
(c) Shear waves are split. (d) P waves undergo refraction.
6. A dynamic range of 60 dB in power corresponds to an increases in amplitude by a factor of ______.
7. The slope of the Wadati plot obtained using the P and S arrival times of a local earthquake is 1.0 The corresponding Vp/Vs ratio of the subsurface medium is _________.
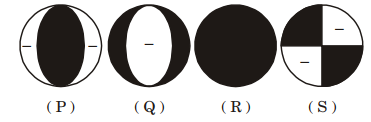
8. The beach ball figure given below depicts the focal mechanism of an earthquake. The shades and unshaded portions indicate compressional and dilatational quadrants, respectively. FP1 is the fault plane solution. The focal mechanism and FP1 represent
(a) a thrust fault with strike 45° and 30° with the tension axis in the compression quadrant. (b) a normal fault with strike 45° and 30° with the tension axis in the compression quadrant. (c) a thrust fault with strike 225° and 60° with the tension axis in the compression quadrant. (d) a normal fault with strike 225° and 60° with the tension axis in the compression quadrant.
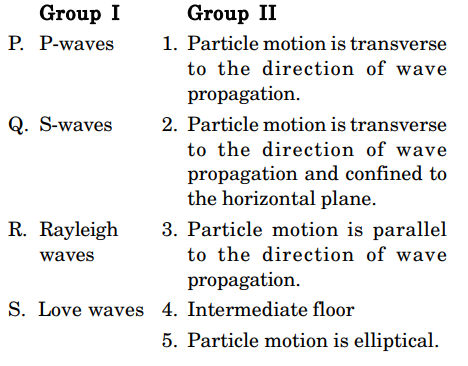
9. Match the items listed in Group I with their respective analytical expressions in Group II.
(a) P-2; Q-3; R-4; S-1 (b) P-2; Q-4; R-1; S-3
(c) P-4; Q-2; R-5; S-3 (d) P-4; Q-3; R-1; S-5
GATE 2018
1. For a layered isotropic medium with a flat horizontal free surface, match the wave types listed in Group-I with their corresponding polarizations listed in Group II
(a) P-1; Q-3; R-4; S-2 (b) P-3; Q-1; R-4; S-2 (c) P-3; Q-1; R-2; S-4 (d) P-2; Q-3; R-1; S-4
2. The unit of shear modulus (rigidity modulus) is
(a) kg m– 1 s– 2 (b) m2 s– 2 (c) kg m– 2 s– 2 (d) m– 1
3. Assume a flat earth with crustal thickness of 35 km and average crustal and upper mantle P-wave velocities of 6.4 km.s– 1 and 8.1 km.s– 1, respectively. The minimum distance from the epicenter of a near surface earthquake at which Pn -waves are observed is _______ km.
4. A solution to the eikonal equation \(|\nabla \tau|=\frac{1}{V_0}\) for homogeneous and isotropic medium in cartesion coordinates is
5. There is a change in t he values of t he bulk modulus and density across the Gutenberg discontinuity (from mantle to outer core). Which one of the following statements is CORRECT?
(a) Both bulk modulus and density increase.
(b) Both bulk modulus and density decrease.
(c) Bulk modulus decreases and density increases.
(d) Bulk modulus increases and density decreases.
6. Using t he Gutenberg-Richter recurrence relationship, the mean annual rate of exceedance of earthquake occurrence in a seismic belt is 0.3 per year for an earthquake of magnitude 6.0. The return period for an earthquake of magnitude 6.0 in this belt is ______ years.
7. The P-wave velocity and the Poisson’s ratio for a homogeneous and isotropic sedimentary rock are 2500 m/s and 0.3, respectively. The S-wave velocity for the rock is ________m/s.
GATE 2019
1. Body waves __________ .
(a) can travel through vacuum (b) have cylindrical wavefronts
(c) are mechanical waves (d) are known as ground roll 5
2. The acceleration due to gravity (g) begins to fall sharply towards the centre of the Earth from the __________ discontinuity.
(a) Conrad (b) Mohorovicic (c) Gutenberg (d) Lehmann
3. Which one of the following lists ONLY kinematic parameters?
(a) Force, translation, rotation.
(b) Translation, rotation, distortion.
(c) Stress, distortion, translation.
(d) Force, stress, strain.
4. The Young’s modulus ‘E’ is related to the Lame’s parameter ‘A,’ for a Poisson solid as
(a) E = 2.5\(\lambda\), (b) E = 1.5\(\lambda\) (c) E = \(\lambda\) (d) E = 0.5\(\lambda\).
5. Which one of the following seismic phases is the earliest arrival in the P shadow zone?
(a) PKiKP (b) PPP (c) P diff (d) PKIKP
6. A shallow focus, Great earthquake with seismic moment of 2.5 × 1040 dyne-cm is recorded at an epicentral distance of 50°. The body wave magnitude (mb), surface wave magnitude (Ms) and moment magnitude (Mw) were estimated. Which one of the following is CORRECT?
(a) mb > Ms > Mw (b) mb = Ms = Mw
(c) mb < Ms < Mw (d) mb < Ms > Mw
7. In a seismogram of a shallow focus (h = 5 km) earthquake, the difference between the arrival times of the S and P phases is 1.34 s. Assuming the average P wave velocity of the crust to be 6.0 km/s and the Poisson’s ratio to be 0.27, the epicentral distance is _____ kilometres, (round off to 1 decimal place).
GATE 2020
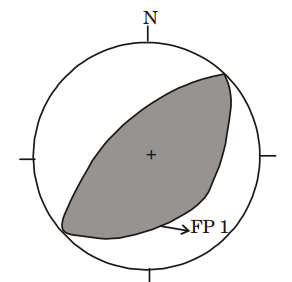
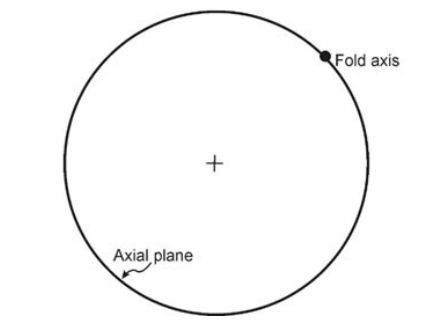
1. The given stereoplot of the axial plane and the axis of a fold represents an/a
(a) upright fold (b) vertical fold (c) reclined fold (d) recumbent fold.
2. Which of the following options shows the internal structure units of the Earth arranged in the CORRECT sequence of increasing volume?